Placeholders
What is a placeholder?
A placeholder represents a variable or piece of data in a workflow. Components pass placeholders to and from each other - they use placeholders from other components to perform an action, and then output placeholders to other components.
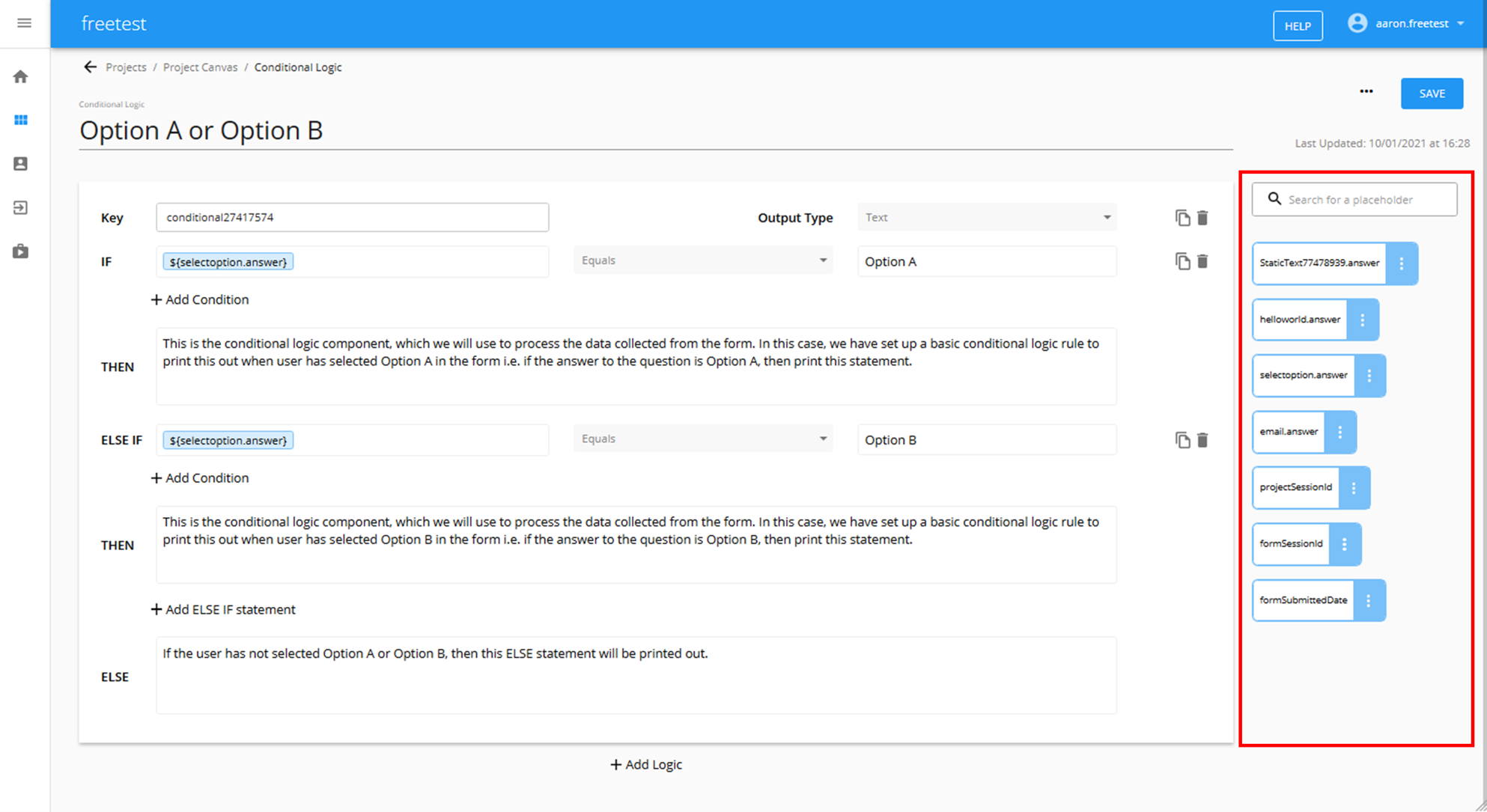
When you are inside a component, you will find the placeholders that can be used on the right hand side.
Inserting placeholders
To insert a placeholder, click in the location where you want the placeholder to be inserted, and then click the placeholder you want to insert using the placeholder menu on the right hand side of the screen
The placeholder will be inserted at the cursor position:
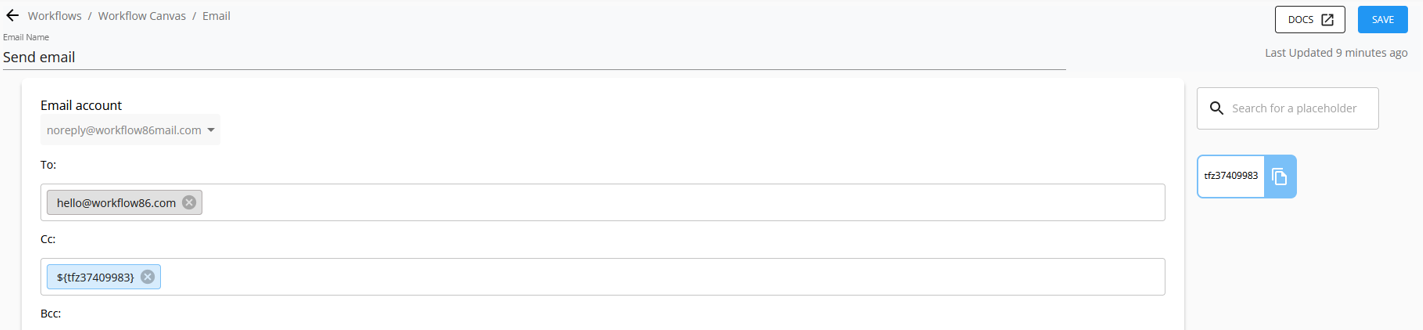
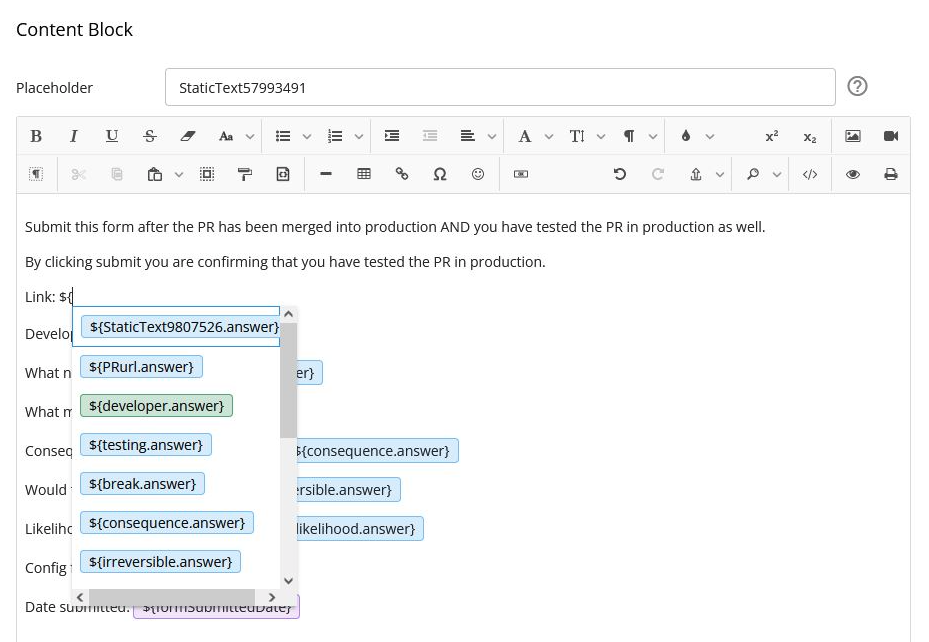
In the Rich Text Editor fields, you can also insert placeholders by typing in "$" to bring up the placeholders, select and then click to insert:
Types of placeholders
Text
A text placeholder represents data that is a series of characters i.e. text, or to be more technical, a string. For example "Hello world"
Number
A number placeholder represents data that is comprised of integers. For example "1234"
List
A list placeholder represents data that is in a list form, that is, it is comprised of a sequence of ordered values or items. For example "A, B, C, D, E".
A list can be a combination of strings or integers.
List placeholders will always be printed with square brackets at the start and end e.g. "[A, B, C, D, E]". To remove the square brackets before printing, you can convert it to text using the List Transform
Datetime
A datetime placeholder represents a date (day, month and year), time (hour, minutes, seconds) and a timezone. The raw value of a datetime placeholder is set according to ISO_ZONED_DATE_TIME.
An example of a datetime placeholder: "2011-12-03T10:15:30+01:00[Europe/Paris]"
HTML
A HTML placeholder represents HTML code, which is typically content with HTML styling (allowing the content to have styling such as bolded text, numbered lists, background colors etc). Any component that is set via a rich text editor field (for example, the rich text editor question type) will output a HTML placeholder.
HTML placeholders must be printed in HTML compatible fields
HTML placeholders need to be printed into HTML compatible fields in order for the style to render correctly. When printed into non-HTML compatible fields, all of the HTML tags and styling will be printed rather than rendered properly.
HTML compatible fields include:
- the body of an email
- the description body of a task
- rich text editor field
- document editor
- content library set to the rich text option
Essentially, any field where you can apply HTML styling is also a field that can accept HTML placeholders.
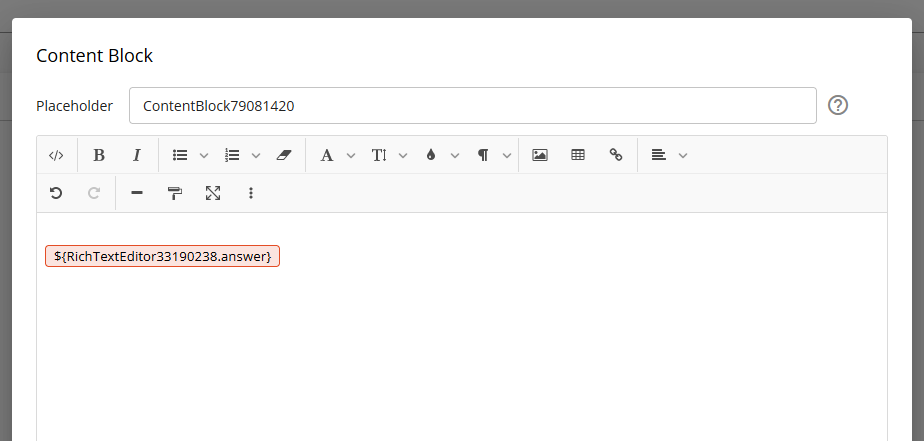
Here is an example of a HTML placeholder being correctly rendered into a content block which is a HTML compatible field
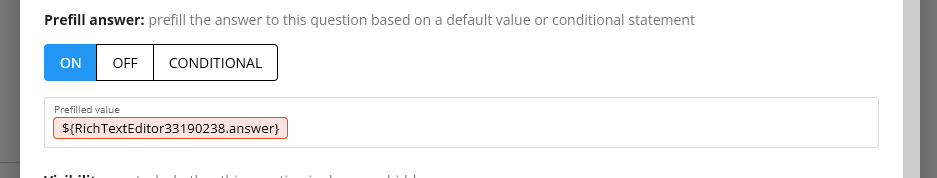
Here is an example of a HTML placeholder being printed into a long text question field which is not HTML compatible:

Broken placeholders
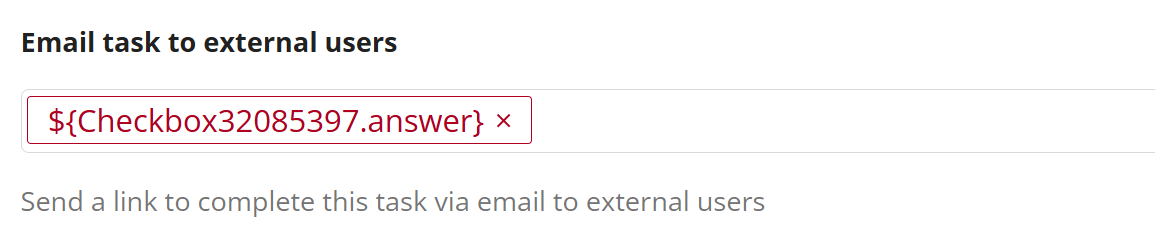
Placeholders which are red are broken meaning that the source of that placeholder can no longer be found because it has been removed or changed. Check whether the placeholder name has been changed e.g. from "Name" to "name". Also check whether the source of the placeholder is still connected into the component.
Turning on the meta-data for forms and tasks and setting a component label will result in any existing placeholders without that pre-fix being marked as broken.